What is the Range in Wavelengths of Visible Light?
When discussing the intricate world of light, one fundamental question often arises: what is the range in wavelengths of visible light? This range is not only pivotal in the realm of physics but also plays a significant role in our everyday experiences, influencing everything from art and design to health and technology. In this blog post, we will delve into the specifics of the visible light spectrum, explore its significance, and understand the implications of its various wavelengths.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
To appreciate visible light, it’s important to first understand its place within the broader electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, ranging from radio waves with wavelengths measured in meters to gamma rays with wavelengths shorter than a nanometer. The visible spectrum is nestled between ultraviolet (UV) light and infrared (IR) light.
Wavelength Range of Visible Light
The range of wavelengths for visible light spans approximately 380 nanometers (nm) to 750 nanometers. This range is divided into different colors, each corresponding to specific wavelengths:
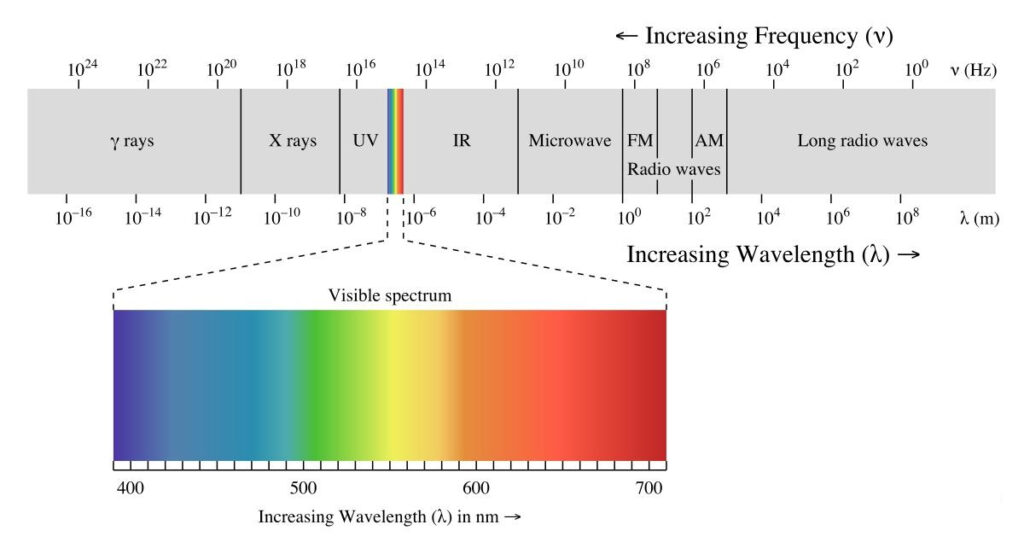
- Violet: 380–450 nm
- Blue: 450–495 nm
- Green: 495–570 nm
- Yellow: 570–590 nm
- Orange: 590–620 nm
- Red: 620–750 nm
Each color has a unique wavelength, and this diversity contributes to the rich palette of colors we can perceive. The ability to see these colors is a result of the way light interacts with objects and how our eyes interpret these interactions.
The Science Behind Color Perception
Color perception is a complex process that involves both the physics of light and the biology of the human eye. Light waves enter the eye and are focused onto the retina, where photoreceptor cells known as cones are activated. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of wavelengths corresponding to red, green, and blue light. The brain then processes signals from these cones to create the perception of color.
Importance of Visible Light
Understanding what is the range in wavelengths of visible light is crucial for several reasons, each highlighting the significance of visible light in our lives:
- Biological Significance: Visible light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. This process is the foundation of life on Earth, supporting the food chain and producing oxygen. Without visible light, the existence of life as we know it would be impossible.
- Human Vision: The ability to see and interpret our surroundings relies heavily on visible light. The cones in our eyes are tuned to specific wavelengths, enabling us to perceive a wide range of colors. This ability enhances our interaction with the environment, aiding in tasks such as navigation, communication, and artistic expression.
- Health and Well-being: Natural light plays a significant role in regulating our circadian rhythms, which govern sleep-wake cycles. Exposure to sunlight has been linked to improved mood, better sleep quality, and overall health. Understanding the wavelengths of visible light can help us optimize our exposure to natural light for better well-being.
- Technological Applications: The properties of visible light are harnessed in various technologies, from LED lighting to optical fibers. Innovations in these fields rely on a deep understanding of light’s behavior and its interaction with materials. This knowledge drives advancements in communication, energy efficiency, and visual displays, making visible light a cornerstone of modern technology.
- Art and Design: In the creative world, the understanding of visible light and color theory is fundamental. Artists and designers utilize the principles of light and color to evoke emotions and create visual harmony. The interplay of light and color can significantly impact how we experience art and design, influencing everything from mood to perception.
The Role of Visible Light in Art and Design
In the fields of art and design, the understanding of visible light and color theory is fundamental. Artists use color combinations to evoke emotions and create visual harmony. Designers consider how light interacts with materials to enhance aesthetic appeal and functionality. The interplay of light and color is a crucial aspect of visual storytelling, influencing how we perceive and experience art and design.
Conclusion
In summary, the range of wavelengths of visible light, from approximately 380 nm to 750 nm, encompasses the vibrant colors that enrich our lives. This spectrum is not just a scientific concept; it has profound implications for our vision, health, technology, and artistic expression. By appreciating the nuances of visible light, we can better understand its significance in our daily experiences and the broader world around us. Whether through the lens of science or the brush of an artist, the beauty and importance of visible light continue to illuminate our lives.
Frequently Asked Question
What is the range of visible light wavelength in micrometers?
The range of visible light wavelengths is approximately 0.38 to 0.75 micrometers (µm), which corresponds to 380 to 750 nanometers (nm).
What is the maximum wavelength of the visible region?
The maximum wavelength of the visible region is about 750 nanometers (nm), which corresponds to the color red.
What is the range of a visible spectrophotometer?
A visible spectrophotometer typically measures wavelengths from about 380 nm to 750 nm, covering the entire visible light spectrum.
What is the range of frequency of visible light?
The frequency range of visible light is approximately 400 terahertz (THz) to 790 THz, corresponding to wavelengths from 380 nm to 750 nm.
What nm range is visible light?
Visible light ranges from approximately 380 nanometers (nm) to 750 nanometers (nm).
What wavelength is blacklight?
Blacklight typically emits ultraviolet (UV) light with wavelengths around 320 to 400 nanometers (nm), just outside the visible spectrum.
Can humans see infrared light?
Humans cannot see infrared light, as it has wavelengths longer than 750 nanometers (nm), which falls outside the visible spectrum.








